Relief checks news summary | 4 May 2023
Follow the latest news on the US economy as Fed increases interest rates; the effect on productivity, jobs, housing prices and the day-to-day of households.

Show key events only
US Finance News: Latest Updates
Headlines | Thursday, 4 May 2023
- Federal Reserve moves to raise interest rates by 0.25 percent, now standing at 5.25 percent
- Fed rate hike drives sell off in Wall Street markets, as investors left uncertain about future policy
- Job openings have fallen by 1.6 million since December
- Layoffs are up twenty-nine percent compared to April 2022; meanwhile, the number of workers voluntarily leaving their jobs has fallen by thirteenpercent
- First Republic Bank acquired by JP Morgan Chase
- World Economic Forum forecasts 14 million jobs disappearing in five years
- Median home selling prices increased 2.6 percent in March
- The rate of families with an unemployed member fell three percent from 2021 to 2022 to 4.7 percent
- Housing prices continue to fall, is it a good time to buy?
- Various states will continue to issue inflation relief checks and generous tax refunds in April
Related stories:
The coronation of King Charles III will be a three-day extravaganza taking place over the weekend, and British taxpayers will be footing the extra-large bill.
Buckingham Palace says there are reports saying the event will bring in more than a billion dollars to the economy, but critics believe the cost will be too high to pay.
Slower job growth expected in April
Employers likely hired the fewest workers in nearly 2-1/2 years in April as the cumulative and delayed effects of higher interest rates start to have an impact on a large part of the economy.
But the Labor Department's closely watched employment report will offer little comfort to Federal Reserve officials battling high inflation, with wage growth expected to have remained fairly strong last month. The unemployment rate is forecast to have risen to a still historically low 3.6%.
The Fed raised its benchmark overnight interest rate by another 25 basis points to the 5.00%-5.25% range on Wednesday, and signaled it may pause the central bank's fastest monetary policy tightening campaign since the 1980s. The Fed has hiked its policy rate by 500 basis points since March 2022.
(REUTERS)
Being a social media content creator continues to be a lucrative occupation. According to the latest list made by Forbes, the highest-paid YouTubers collectively earned around $300 million in 2021. This represents a record amount, 40% more than the previous year.
Ax Corina Gonzalez reports, these gains are primarily driven by increased views on their YouTube channels, as well as the ad revenue they generate from those videos.
A significant number of the top-paying jobs in the US can be found in the health care sector.
This field is experiencing a personnel shortage, believed to have been precipitated by burnout due to the pandemic. To have better chances of drawing in new people and avoid losing existing staff, private health care organizations have crafted attractive salary packages.
This report tells us more on the top-paying jobs in the country.
Mortgages and interest rate rises
Typical mortgage rates in the United States are not specifically tied to the federal funds rate, rather they track the yield on 10-year Treasury Bonds. The value of the bonds is related to the Fed’s economic outlook, and further interest rate hikes do not convey confidence from the central bank.
The Federal Reserve released updated figures for both 15-and-30-year fixed-rate mortgages, which are 5.76 percent and 6.39 percent, respectively. Compared to this time last year, both rates have increased by more than 2.5 percentage points. However, in recent month these rates have softened slightly, compared to the levels recorded when the Fed first began raising rates.
The Federal Reserve has announced yet another interest rate increase, moving the federal funds rate up to 5-5.25 percent. The announcement of another increase which came on 3 May led rates to rise above five percent for the first time since The Great Recession.
We take a look at the consequences for some of the most common types of borrowers...
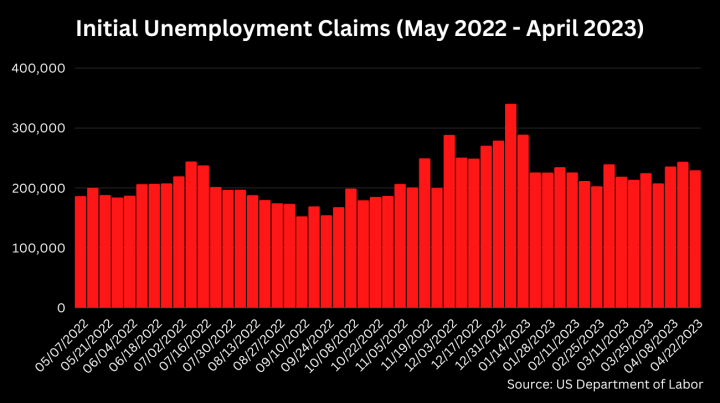
Initial unemployment claims rose last week
Initial unemployment claims increased by by 13,000 to 242,000 the week ending on 29 April. This has moved the 4-week moving average up to 239,250.
Nationally, the insured unemployment rate was 1.2 percent at the end of April. These figures are down significantly, compared to the rates recorded in the year months of the pandemic. In total, 1.8 million people were receiving unemployment benefits for the week ending on 22 April.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) wrapped up its May meeting on Wednesday with a unanimous decision to raise interest rates by another 25 basis points. That’s the tenth hike since March 2022 pushing interest rates above the 5 percent mark for the first time in over a decade. Policymakers have ratcheted up borrowing costs at the fastest pace since the 1980s to tame inflation not seen in four decades.
Chairman Jerome Powell, speaking at a press conference after the meeting, signaled that the US central bank may pause further rate hikes. However, it will assess if more action is needed to bring down inflation on a meeting-be-meeting basis.
Starting at the onset of the covid-19 pandemic, Congress passed a law allowing the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) to boost the amount households received from the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP). Lawmakers, however, voted to end the Emergency Allotments (EA) as they were known as part of the Omnibus spending bill passed at the end of 2022.
While the SNAP EA program was in place it is estimated that it kept 4.2 million people out of poverty and reduced childhood poverty by 14 percent. As of 1 March, SNAP EA benefits ended in the 32 states that were still paying them along with the District of Columbia, Guam and the US Virgin Islands.
Households saw their monthly allotment drop by $95 on average, some will lose hundreds of dollars to put nutritious food on the table. For those that benefited from the increased payments, they will now have to make hard choices about what they spend their money on as the cost of living has increased. That will mean cutting back on how much they eat or putting off paying bills so they can put food on the table.
Federal Reserve Governor Lisa D. Cook spoke publically last week about the state of economic research and the current questions that exists for many tracking changes in the US economy. Governor Cook called attention to what she sees as signs that the labor market is “softening,” including a slowdown in the quit rate and hiring a reduction in the number of job openings. From December to March, the number of job openings fell by 1.6 million to 9.6 million.
Specifically, Gov. Cook’s comments mentioned the ‘strong’ increase in wages seen for “workers in the lowest-income quartile [...] relative to other quartiles over the past two years.” With far more jobs than workers seeking then, Gov. Cook said that this group “benefitted from the availability of jobs and, in many cases, the ability to move to better, higher-paying jobs in the current strong labor market.”
Read our full coverage for more details on the relationship.
The Federal Reserve has been raising interest rates at the fastest pace since the 1980s driving up the cost of borrowing for buying a home or car, as well as making carrying a balance on your credit card costlier. When looking at getting a new credit card or loan you’ll come across the terms “APR” and “interest rates” that many use interchangeably.
However, they have some key differences.
More than two years have passed since the US federal government approved the third and last stimulus check. The payment was part of the March 2021 American Rescue Plan and offered a $1,400 check for eligible taxpayers and up to $2,800 for couples filing jointly.
Since then, millions of Americans have been waiting for a fourth stimulus check, and although the measure was never approved at the federal level, various states decided to send their own checks to residents. Below we will discuss which states can expect a direct payment in May and June.
The Federal Reserve since March 2022 has been tightening monetary policy including successive interest rate hikes to tame rising prices. Inflation in the United States has been slowing but isn’t expected to reach the US central bank’s target of two percent until at least 2025. Experts don’t rule out more rate hikes, especially if macroeconomic data stays strong, and most don’t forecast any cuts before the end of the year.
Minutes from the March meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) expressed concern over inflation which is “still well above the Committee’s longer-run goal of 2 percent” and the it is “unacceptably high.” The data on price pressures in the economy “indicated slower-than-expected progress on disinflation.”
But interest rate change remains a blunt tool to tackle a nuanced economic issue and its use doesn’t come without some pain. However, “the worst pain would be if we failed to act,” according to the Fed chair. We take a look at some of the consequences of the interest rate hike and how it could affect you…
Forbes has revealed its list of the richest people in the world in 2023. Find out who the five richest Latinos are and how they made their fortunes.
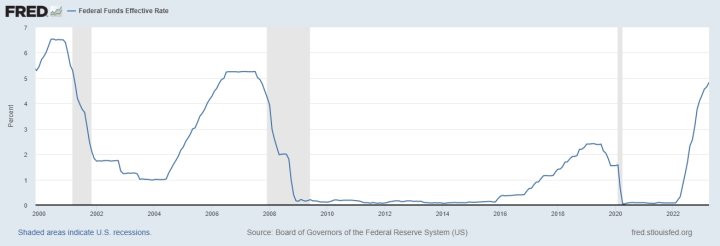
Interest rates hit highest level since 2007
For the first time in over a decade, the federal funds effective rate (FFER) has surpassed five percent.
The Federal Reserve announced another rate hike of 0.25 percent, leaving the FFER between 5 and 5.25 percent.
Some economists had called on the central bank to slow the pace of its rate increases in light of the the collapse of First Republic Bank. However, the Fed seems to have their own view, affirming that from their vantage point "The U.S. banking system is sound and resilient."
Pacific Western Bank shares tumble
Another regional bank appears to be in trouble.
Shares of Pacific Western Bank have plunged 56% following reports that it is considering its strategic options, including a possible sale.
The turmoil at PacWest follows on the heels of the sale of First Republic Bank to JP Morgan Chase, and the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank and Signature Bank in March.
Due to inflation, several states in the US approved the sending of stimulus checks or tax refunds as relief last year. Since then, inflation has fallen; however, financial support continues in certain locations, with payments of up to $1,500.
This report tells us which states give out financial aid, and who are qualified to receive it.
Last year, the inflation rate reached historic levels in the United States. In June 2022, the year-on-year rate was 9.1%, the highest in the last 40 years.
After its peak, inflation began to fall. According to the latest summary of the Consumer Price Index, in March, year-on-year inflation was 4.98%. However, the prices of some items are still high.
Corina Gonzalez tells us when we can expect prices to slide back down.
Tuesday Morning to close all stores
Home goods retailer Tuesday Morning has gone bust and will close all of their stores.
They have announced a going-out-of-business sale with 30% discounts in all their stores, which number approximately 200.
Tuesday Morning has joined the growing number of troubled retailers who are going bankrupt due to slower consumer spending, combined with more expensive debt caused by higher interest rates.
Last week, Bed Bath & Beyond filed for bankruptcy and also declared that they were shutting down all their stores.
Top CEO salary raises outpace inflation
The average pay for top CEOs rose 7.7% last year to a record $22.3 million, a new study found, as big stock awards helped the group stay ahead of inflation while workers' pay fell behind.
Among those receiving big pay increases were the CEOs of Jefferies Financial Group and Prologis Inc according to the study released by research firm Equilar.
The study reviewed the 100 highest paid CEOs at public companies with revenue of $1 billion or more that reported compensation as of March 31. A similar review last year showed a 31% pay increase for CEOs for 2021.
The consumer price index, a widely-used measure of inflation, rose 6.5% in the 12 months ended Dec 31, down from 7% in the year-earlier period.
Pay among the CEOs rose faster than for workers in 2022 despite tight labor markets. Average weekly earnings for private sector employees was $1,132 in December, up 3.6% from a year earlier, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The CEOs´ higher gains pushed the median "pay ratio" at companies led by the CEOs studied by Equilar to 288 times the pay of their average employee, up from 254 times in 2021.
(REUTERS)
For the second year in a row, both the number of billionaires worldwide and their total wealth have declined. According to Forbes, in 2023 , the number of billionaires fell from 2,668 in 2022 to 2,640 this year. On the other hand, the total wealth of billionaires dropped by $500 billion.
As for the number of billionaires in the world, most of the members of the Forbes list are from the United States with 735 billionaires. The US is followed by China (495), India (169) and Germany (126). The richest person in America is Elon Musk from Texas, but who are the billionaires in the rest of the country?
Writers guild trying to save jobs from AI and get better pay
The Writers Guild of America (WGA) began its largest strike in 15 years, not only to secure better pay as streaming continues to disrupt Hollywood but to protect their jobs from artificial intelligence (AI). Several shows have already been affected and depending on the length of the strike many others could be too.
According to WGA statistics, median weekly pay for writer-producers has decreased by 4 percent over the last decade, when adjusted for inflation it’s a decline of 23 percent. The median number of TV series writers working at the minimum salary has gone from a third in the 2013-14 season to half nowadays.
The writers guild also wants to prevent studios from using AI to generate scripts. Either producing new material which writers may be asked to polish up for less pay or training the machines on writers’ previous work to create new scripts in a specific writers style.
"We don't want our material feeding them, and we also don't want to be fixing their sloppy first drafts," said John August, a screenwriter and member of the WGA negotiating committee.
“What (AI) could do is spew out a garbled piece of work," said Warren Leight, a screenwriter who has also served as a showrunner and executive producer. "Instead of hiring you to do a first draft, (studios) hire you to do a second draft, which pays less. You want to nip that in the bud."
Welcome to AS USA’s live blog on the latest financial news
Throughout the day we'll bring you news on personal finance and the wider US economy.
The Federal Reserve raised rates by an expected 25 basis points on Wednesday. However, markets reacted poorly as uncertainty about the future central bank policy leaves investors in limbo.
The Fed's goal of reducing inflation to 2% isn't predicted to be accomplished until 2025 while a possible recession could hamper those efforts. In the meantime households are still struggling with rising prices but inflation relief programs are coming to an end.

/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/diarioas/QV6THY6I2NCSXARZ6GVQ6LFAJY.jpg)
/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/diarioas/YPR7NKNNXZOMPFBPWLHSLJAJ7A.jpg)











/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/diarioas/SQ2V2BRRZZLPVA6WJVWPLDKWVA.jpg)
