Earth Overshoot Day: what does it mean and when does it happen?
Research from the WWF and the Global Footprint Network suggests that we are currently using resources 75% faster than the planet can regenerate them.

Natural resources are a precious commodity, but they are not unlimited. Each year the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) calculates a point known as Earth Overshoot Day, the date on which the world has used up a year’s supply of natural resources.
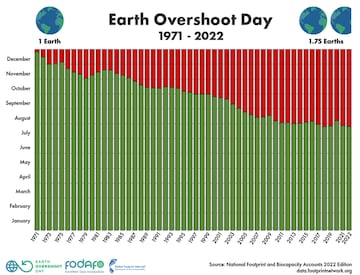
In an ideal world that point would fall late on 31 December every year, allow the planet to replenish resources at a sustainable rate. However the trend shows that Earth Overshoot Day is coming along earlier every year, falling on 28 July this year. From now on, the Earth is in the red.
The WWF states that to cover our needs for the whole year we would need to be producing around 175% of our current yield from natural resources.
“In economic terms, it would be like exhausting the available balance and going into the red,” explains the WWF.
But not all countries deplete these resources in a similar way and the most developed nations typically use up the world’s resources more quickly. According to the WWF we would need the resources of five planets to cover the demands if the entire global population used up resources at the rate of the average American.
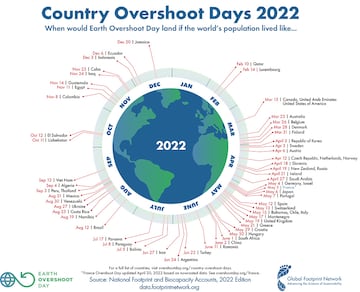
This graph shows how consumer patterns vary in different countries, and which reach their own Overshoot Day earliest.
What is Overshoot Day?
According to the WWF, Overshoot Day is the date “on which the demand for ecological resources and services of humanity in a specific year exceeds what the Earth can regenerate in that year”.
The exact day on any given year is calculated by the Global Footprint Network, an international research organization. For its calculation the GFN analyses the biocapacity (biological regeneration capacity) and the ecological footprint (the demand for resources) of the planet.
The first country to exhaust capacity this year was Qatar, which only needed 40 days (February 10) to consume the resources. At the other end of the spectrum, Jamaica will not have exhausted its resources until 20 December.
The global Earth Overshoot Day is of particular concern at a time when extreme temperatures, forrest fires and ocean-warming is becoming more pronounced. In the past 50 years, Earth Overshoot Day has been brought forward by nearly half a year: from December in 1971 to the current month of July.
Enrique Segovia, conservation director of WWF Spain, says that this day should remind us that the current model of production and consumption is one of the great causes of the destruction of nature and the climate crisis.
He says: “We can all help stop the ecological deficit by making better decisions in our daily lives”.






